Jiahao Xia, Hongbin Li, Huaping Xu
Acta Polym. Sin., 2020, 51, 205.
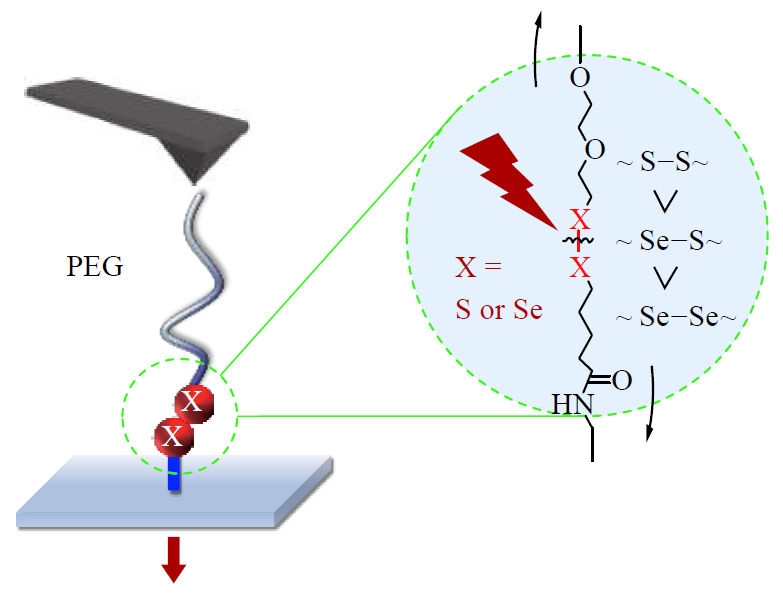
Sulfur, selenium-containing bonds, including disufide bond (SS), diselenide bond (SeSe), and selenide-sulfide bond (SeS), are an important type of light responsive dynamic covalent bonds. Among them, SS and SeS bonds can undergo exchange reaction with the irridiation of UV light, while SeSe bond only requires visible light due to its weaker bond energy. The purpose of this research is to use atomic force microscope-based single molecule force spectroscopy (AFM-SMFS) measurement to reveal the reasons behind the responsiveness and stability of S/Se related dynamic covalent bonds. In this study, quartz substrates modified by SS or SeSe bond were prepared via surface modification. Specifically, the quartz substrates were first washed with a mixture of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide (volume ratio is 7:3), and then processed with oxygen plasma to obtain a hydrophilic surface. The surface then reacted with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane to form amino groups at the top, which further reacted with disulfide or diselenide containing diacid to afford SS or SeSe bond-modified substrates. The structures of the surfaces were comfirmed by water contact angle (WCA), atomic force microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. Based on the light induced exchange reaction, wettabilities of the substrates were able to adjusted and were characterized by WCA and XPS. By exchanging with thiol or diselenide containing polymer, the polymer chain-attached substrates linked by a single bond of either SS, SeS, or SeSe could be obtained. The rupture forces of the three bonds were measured by SMFS. At a pulling speed of 200 nm/s, the rupture forces of SeSe, SeS and SS bonds were (1100 ± 300), (1320 ± 330), and (1450 ± 300) pN, respectively, indicating their strengths decreased as SS > SeS > SeSe. This result was consistent with the thermodynamic stability ranking of the three bonds. SMFS results illustrated that the strength of the dynamic covalent bond is between that of non-covalent interaction and that of robust covalent bond (e.g. C―C bond), which accounts for its balance of responsiveness and stability.