Jinyan Si, Chaowei He and Huaping Xu*
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces; 2025, 17, 37090
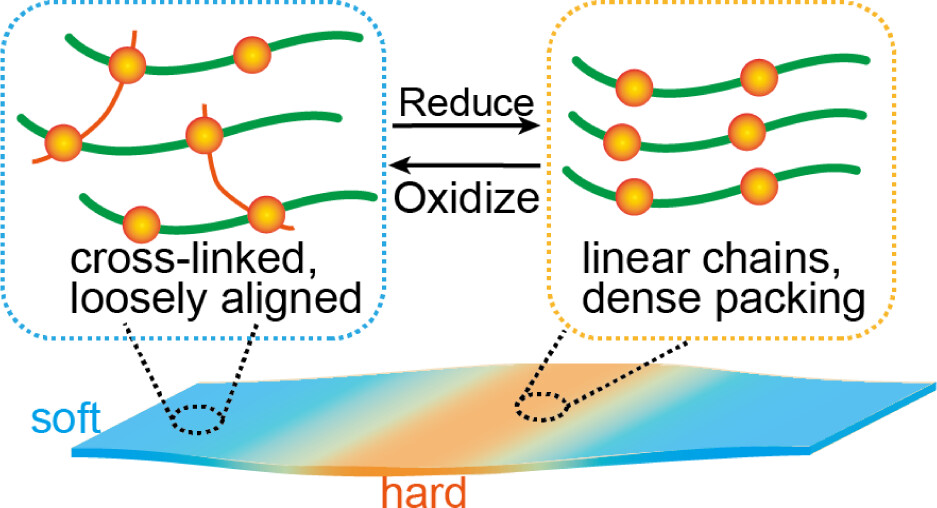
Strain isolation strategies are widely employed in flexible electronic device fabrication to enhance their stretchability. One common approach involves modulating the cross-linking degree of the materials to create regions with a heterogeneous modulus. However, existing materials typically rely on permanent cross-linking networks, which restrict their recyclability and environmental degradability. In this study, we introduce a recyclable thermosetting tellurium-containing polyurethane (TeHPU) as a substrate for flexible electronics. Upon oxidation, this material undergoes a transition into a cross-linked thermoset polyurethane. Intriguingly, the oxidized polymer elastomer exhibits a reduced modulus, which can be attributed to the decreased crystallinity. By spatially controlling the oxidation pattern of the TeHPU film, we achieved precise modulation of high- and low-modulus regions. This resulting material demonstrates potential as a flexible electronic substrate, effectively reconciling the competing demands of robust electronic component adhesion and large-scale deformation. Furthermore, the cross-linked polyurethane network can be chemically reduced back to its thermoplastic state, enabling recycling and reprocessing. This work addresses the recyclability of flexible electronic substrates and provides a new strategy for tuning the Young’s modulus of polyurethane, paving the way for sustainable and eco-friendly electronic devices.