Yuanbo Zhang, Chaowei He, Huaping Xu*
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces; 2025, 17, 13324
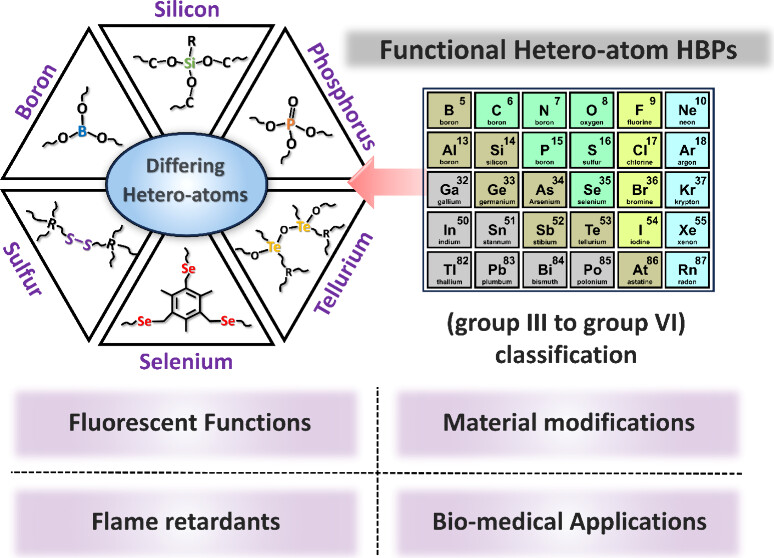
Heteroatom-substituted hyperbranched polymers (HBPs) have emerged as a versatile class of functional materials, combining the structural merits of hyperbranched architectures with the unique chemical functionalities imparted by heteroatoms such as boron, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. These polymers exhibit distinct physicochemical properties, including low viscosity, excellent solubility, high chemical reactivity, and tunable functionality, which position them as promising candidates for diverse applications. This Review highlights the recent advances in heteroatom substituted HBPs, categorizing them from the element group of their heteroatoms (from Group III to Group VI, as well as transition and rare-earth metals). The pivotal role of heteroatoms in modulating polymer properties is explored, with key applications highlighted across four principal domains: fluorescent materials, flame retardants, stimuli-responsive polymers, and polymer modifications. By integrating insights from chemistry, materials science, and interdisciplinary research, this Review underscores the potential of heteroatom-substituted HBPs in addressing current material challenges.