Feng Li, Yiye Li, Xiao Yang, Xuexiang Han, Yang Jiao, Taotao Wei, Dayong Yang, Huaping Xu and Guangjun Nie
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 2377-2382
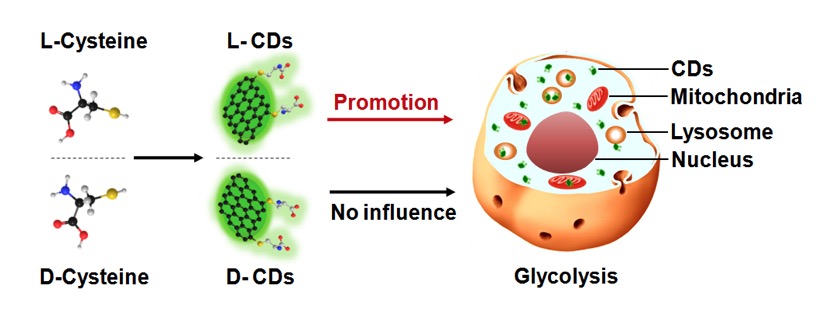
Cysteine-based chiral optically active carbon dots (CDs) and their effects on cellular energy metabolism, which is vital for essential cellular functions, have been barely reported. A green and effective synthesis strategy for chiral N-S-doped CDs (fluorescence quantum yield ca. 41.26 %) based on hydrothermal treatment of lord-cysteine at as low as 60℃ has been developed. This suggested that cysteine was instable in aqueous solutions and acts as a warning for high-temperature synthesis of nanomaterials using cysteine as stabilizer. Human bladder cancer T24 cells treated with L-CDs showed up-regulated glycolysis, while D-CDs had no similar effects. In contrast, no disturbance to the basal mitochondrial aerobic respiration of T24 cells was caused by either chiral CD.