Banruo Xianyu and Huaping Xu*
Supramolecular Materials; 2024, 3, 100070
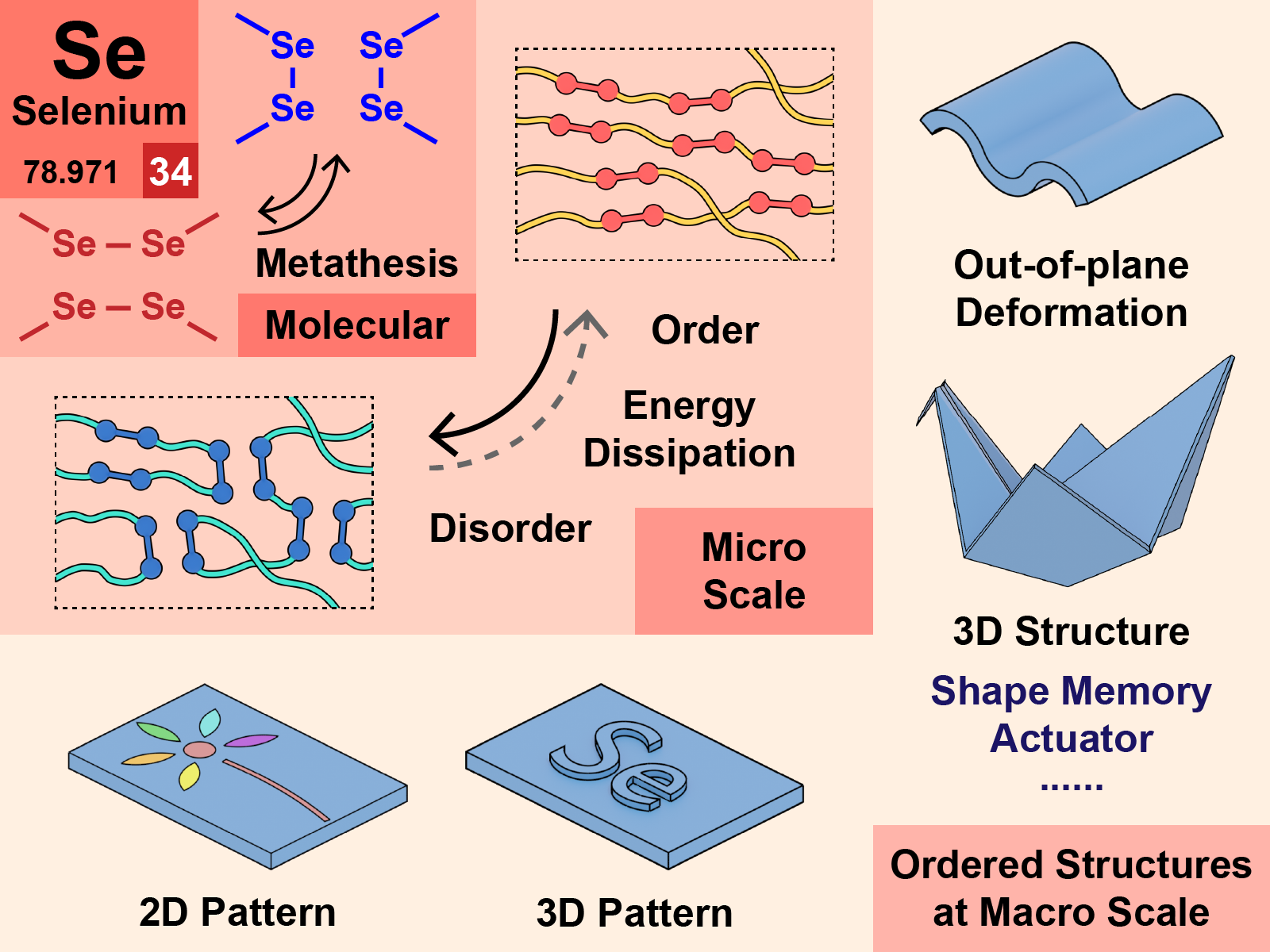
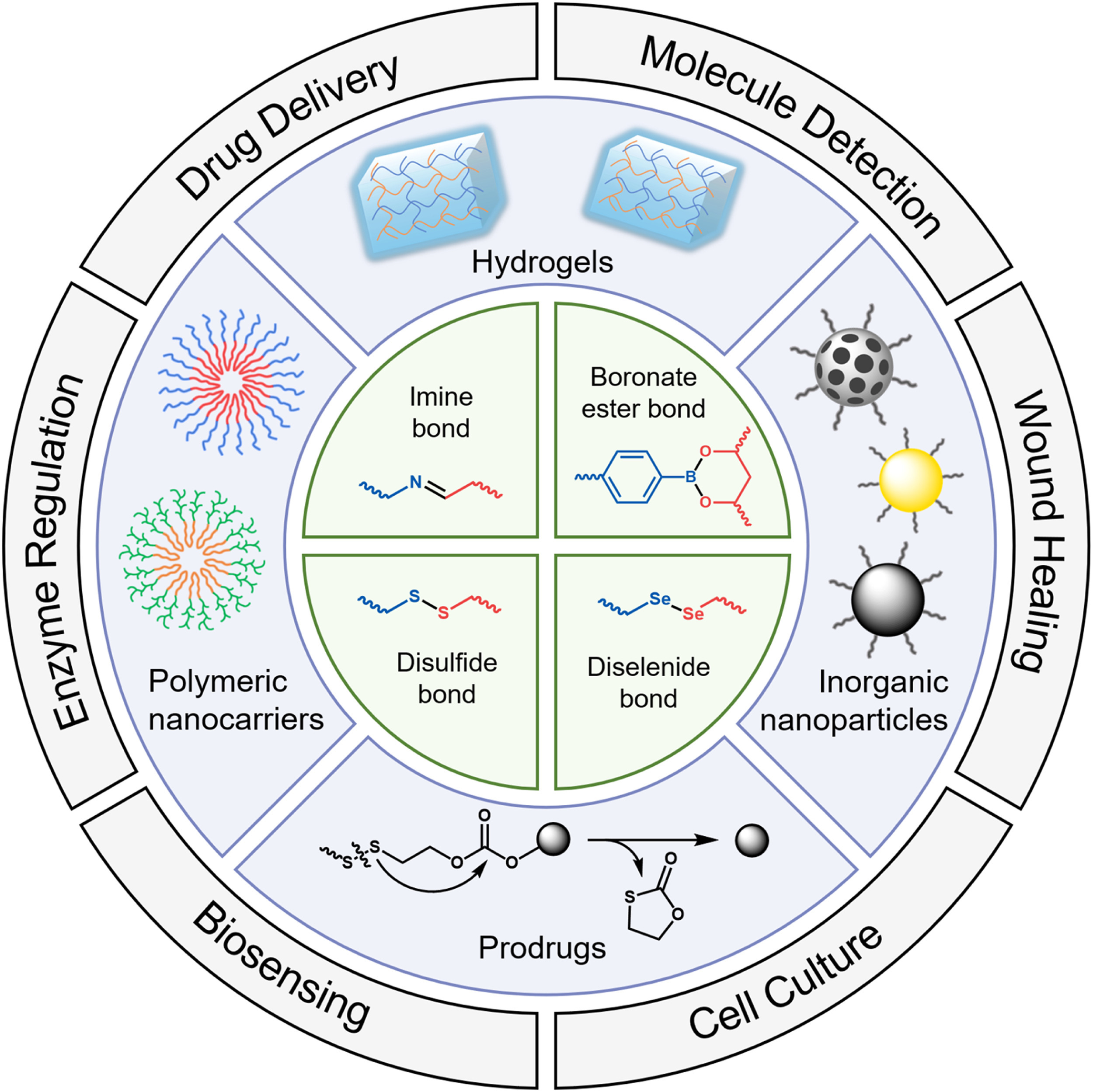
Dynamic covalent bonds (DCBs) have received significant interest due to their unique reversibility and stimuli-responsiveness. The introduction of DCBs provides materials with self-healing and controllable load and release properties, which result in the emergence of widespread applications in biomedical disciplines. In this minireview, we first introduce the chemistry nature and reaction characteristics of different types of DCBs followed by discussing the design strategies of DCB materials. Finally, we summarize the la...
More